Tracheal Stenosis
Tue, 16 Jan 2024
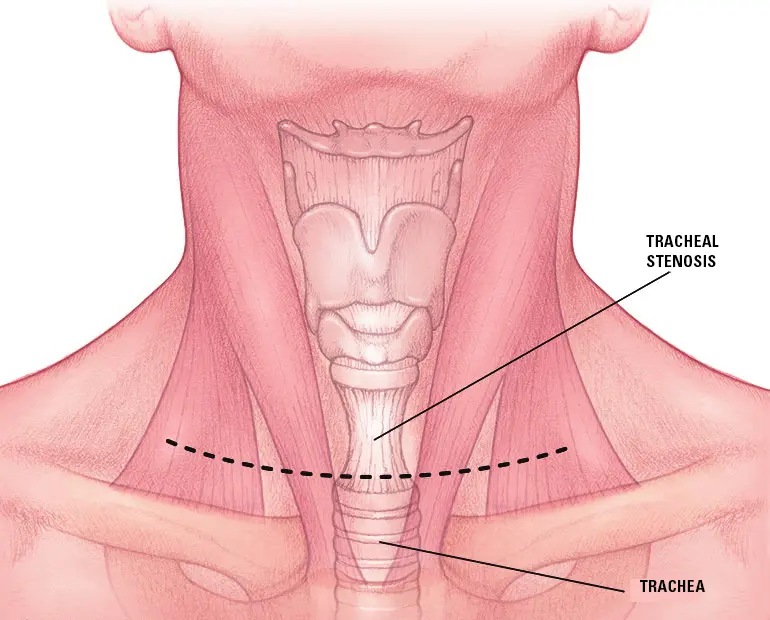
Tracheal Stenosis
A medical condition known as tracheal stenosis causes the trachea, the airway that links the voice box, or larynx, to the lungs, to become abnormally narrowed or constricted. Breathing might become challenging as a result of this constriction. If not treated appropriately, tracheal stenosis can be a fatal condition. Consult the Best Lung transplant surgeon in India to learn more about its treatment options.
Tracheal stenosis is a narrowing or constriction of the trachea. Most cases of tracheal stenosis develop when a persons trachea is injured after prolonged intubation - when a breathing tube is inserted into the trachea to help maintain breathing during a medical procedure - or from a tracheostomy (surgical opening of the trachea).
Tracheal stenosis can also develop from a number of other causes, including external injury to the throat; when a benign or malignant tumor presses on the windpipe; certain autoimmune disorders (polychondritis, sarcoidosis, papillomatosis, amyloidosis and Wegeners granulomatosis); and infections (bacterial and fungal infections as well as tuberculosis). It can also develop as a side effect of radiation therapy when administered to treat a tumor in the head or neck.
Causes Of Tracheal Stenosis
There can be several causes of tracheal stenosis, including:
- Trauma: severe injuries to the chest or neck, including those caused by falls or vehicle accidents, can harm the trachea and cause scar tissue to develop, which narrows it.
- Intubation: The tracheal lining can become irritated and damaged by long-term exposure to a breathing tube (endotracheal tube) in surgery or in intensive care applications leading to stenosis.
- Infections: Serious infections affecting the trachea or adjacent tissues may result in swelling and scarring, which may progress to stenosis.
- Tumours: In the trachea or surrounding tissues, malignant or benign tumours may compress and constrict the airway.
- Autoimmune diseases: The trachea may become inflamed or suffer damage from illnesses like Wegeners granulomatosis or relapsing polychondritis.
Symptoms of Tracheal Stenosis
A variety of uncomfortable symptoms can result from tracheal stenosis. These may consist of:
- Breathing Problems: Shortness of breath is a typical symptom, particularly when exercising or when lying down.
- Wheezing: The constricted airway may cause a whistling sound that is high-pitched when breathing.
- Noisey Breathing (Stridor): An audible, jarring, vibrating noise while inhalation or exhalation may be an indication of a blockage of the airway.
- Coughing: The discomfort brought on by the limited airflow may lead to persistent coughing.
- Swallowing Difficulties: Tracheal stenosis may impact the nearby oesophagus, causing swallowing problems.
- Recurrent respiratory infections: diseases are caused by frequent respiratory illness, which is made more likely by a weakened airway.
- Chest Pain: People occasionally may feel pain or discomfort in their chests.
- Cyanosis: Due to oxygen depletion, severe stenosis can cause cyanosis, a blue colouring of the skin.
Various factors, including the degree of tracheal constriction, underlying reasons, and individual characteristics, might affect the intensity and mix of these symptoms.
- shortness of breath, coughing, wheezing, difficult or labored breathing (dyspnea)
- difficult-to-treat asthma diagnosed in an adult, stridor (a high-pitched sound that can be heard as the breath is drawn in and is caused by a blockage in the throat or voice box)
- frequent inflammation of the lungs (pneumonitis) or recurrent respiratory infections
- fatigue and general feeling of discomfort (malaise)
- cyanosis (bluish color in the skin or mucous membranes in the mouth or nose).
Diagnosis of Tracheal Stenosis
The diagnosis is by CT scan of the neck and chest and bronchoscopy. A combination of factors is often used to diagnose tracheal stenosis.
- Medical History: Your healthcare provider will inquire about your symptoms, your medical background, and any past trachea-related operations or treatments.
- Physical exam: Your physician may pay attention to your breathing and look for indications of respiratory distress.
- Imaging Studies: Detailed pictures of the trachea can be obtained through X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs, which can be used to pinpoint the precise position and degree of stenosis.
- Bronchoscopy: A bronchoscope, a small, flexible tube containing a camera, is inserted into the mouth or nose to provide a direct view of the trachea during bronchoscopy. Tissue samples (biopsies) can also be taken using this method.
Tracheal Stenosis Treatment Options
The severity of the problem and its underlying cause determine the best course of action for tracheal stenosis:
- Medical Management: Medication to lower inflammation and regulate symptoms may be used to address mild instances of tracheal stenosis. This method is frequently short-term and used to get ready for additional therapies.
- Endoscopic procedures: These can be utilised to enlarge the tracheas restricted region in less severe circumstances. Such procedures might entail removing scar tissue with a laser or balloon dilation).
- Placement of a Stent: For keeping the trachea open in cases of severe stenosis, a mesh tube or stent can be implanted. Depending on the patients condition, stenting might be either temporary or permanent.
- Surgery: surgical treatment may be required in situations of severe tracheal stenosis. The constricted segment can be removed, and both normal tracheal ends can be reconnected, using techniques like tracheal resection as well as reconstruction or laryngotracheal reconstruction.
- Tracheostomy: An artificial airway can be made below the stenosis via a tracheostomy, which may be used in emergencies or where conventional therapies are impractical.
The condition known as tracheal stenosis is characterised by the constriction of the trachea, which can cause breathing problems. Despite the fact that its causes might vary, early detection and the right course of action are essential for controlling the illness and raising the individuals quality of life. If you encounter any tracheal stenosis-related symptoms, immediately speak with a specialist (Dr. Arvind Kumar) medical practitioner for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
The treatment consists of dilation (stretching) of the narrowed segment by specialized medical balloons or surgery. Our unit specializes in this complex procedure and we get patients from all over the country and neighbouring countries.
Videos
Tracheal Stenosis Patient Experience Video - Dr. (Prof.) Arvind Kumar
Tracheal Stenosis Patient Experience | Surgery for Difficulty in Breathing