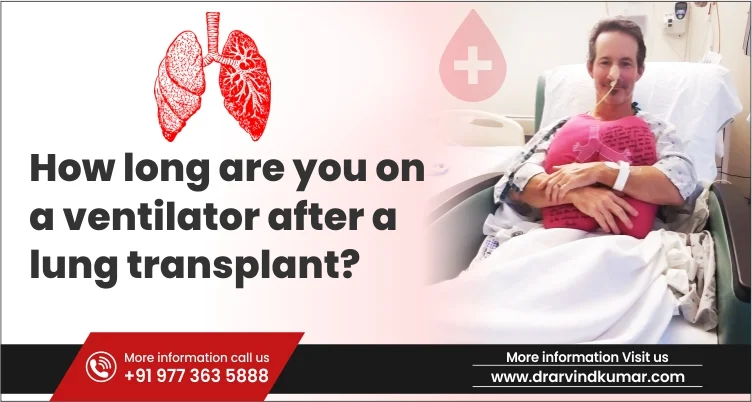
Life after a lung transplantation procedure transcends into an entirely new dimension. You finally have two working and fully functioning lungs that won’t disappoint you or make you suffer each day of your life.
However, reaching that level of comfort and attaining that quality of life involves a lot of subsequent stages. Thinking that life suddenly gets better after a lung transplant is wishful thinking. Instead, it involves a lot of ups and downs.
Being on ventilator support after a lung transplant is mandatory for life support until the transplanted lungs are strong enough to support the breathing capacity of the patient.
This article will explore everything you need to know about being on a ventilator after a lung transplant. Lung Transplant Recovery
What is the Significance of Mechanical Ventilation in Lung Transplant Patients?
Following the successful completion of the lung transplantation surgery, the patient is normally wheeled into the recovery ICU unit, where they are kept under prolonged observation.
During this time, the patient is also connected to a mechanical ventilator that helps them breathe. Simultaneously, the patient is also connected to multiple tubes in the chest to drain the fluids from around the lungs and the heart.
The significance of mechanical ventilation is indispensable both for intraoperative and post-operative support after lung transplantation. Most lung transplant patients are often at risk of developing acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), which is why mechanical ventilation is a must-have after surgery.
How long the patient stays on the mechanical ventilator support differs from one patient to the other. Typically, it lasts for a few days after the lung transplant in india surgery or until the patient’s transplanted lungs are strong enough to function independently.
The doctor will closely monitor the recovery of the patient post-surgery and determine when they are healthy and strong enough to breathe on their own. Following that, the patient is transferred to the ICU.
Recovery following that takes between one to three weeks at the hospital. However, this isn’t a definite period and is subject to change depending on how well the patient is recovering.
When does the Patient End up Ventilator Dependent with Tracheostomy?
Before discussing the need for a ventilator and tracheostomy in lung transplant patients, let us understand what tracheostomy is.
A tracheostomy is a “surgical airway management procedure”, wherein the surgeon creates an opening in the front of the neck, through which a tube is directly inserted into the windpipe to support the regular respiratory functions of the patient. It reduces the work of breathing and allows for
Now, the question is, “Why would a lung transplant patient need a ventilator alongside tracheostomy?”
Despite optimal care and precise practice, there are always some odds that the doctor and the patients are playing against.
Following a lung transplantation surgery, there are chances that some critically ill or high-risk patients might experience issues regarding poor oxygenation and labored breathing. Situations like these call for an immediate mechanical ventilator dependency along with tracheostomy. It reduces the work of breathing and allows the removal of pent up secretions which help the patient breathe better.
Is it possible for Lung Transplant Patients to be on Ventilation for up to 6 months?
Before you get scared or confused looking at this predicament, kindly remember that this is an extremely rare condition.
At most, the majority of lung transplant patients have to be on a mechanical ventilator for the duration of their hospital stay during their recovery period.
Only in extremely high-risk or terminal cases with post-transplantation complications will you witness the patient on mechanical ventilation for up to 6 months after their lung transplantation surgery.
What are Some Long-Term Adjustments Needed after a Successful Lung Transplant?
Simply knowing how long on the ventilator after lung transplant isn’t enough, especially if you are figuring out the recovery procedure after the surgery.
A huge part of the recovery process after a successful lung transplant is to introduce realistic long-term adjustments in your life.
Some of the most important ones include:
1. Being on Immunosuppressants
Every lung transplant patient has to be on some degree of immunosuppressant. Although these start out with extremely high dosages right after the surgery to prevent chronic rejection, the doctors will make salient adjustments as the patient is recovering. However, irrespective of the changes in dosage, immunosuppressants are a lifelong commitment for a lung transplant patient and they have to be on them as prescribed to prevent any risks of organ rejection down the line.
2. Being on prescribed medications and therapy
Not just immunosuppressants, a lung transplant patient also has to be on a variety of medications and therapies life-long. Following the doctors advice to the T is crucial for a healthy life and progressive recovery after such a life-altering procedure. You’d have to check and monitor lung functions at home and go for follow-up consultations as advised.
3. Following a healthy lifestyle
Another important aspect of recovery after lung transplantation is to live a healthy lifestyle. Not only does it involve a healthy diet, but it also includes eliminating ill habits like smoking, drinking alcohol, etc. Besides that, indulging in exercises and leading an active lifestyle are also quintessential to a lung transplant patient’s well-being. Some patients might need to undergo pulmonary rehabilitation as well.
4. Getting Emotional Support
Although lung transplantation drastically improves one’s quality of life, we can’t deny the fact that undergoing such a tedious process can be quite taxing on one’s mental health. Hence, ensuring that you have a healthy outlet for stress and negative emotions is crucial to a patient’s recovery as well.
Conclusion
Lung transplantation is a highly sensitive and life-altering procedure that involves a lot of precautions, expertise, and after-care during the recovery. Being on a ventilator during that period of initial recovery is essential, especially due to the fact that it supports one’s respiratory functions until the transplanted lungs are strong enough to function independently.
Having a clear understanding of the procedure and the post-operative recovery, including the need for a mechanical ventilator is thus vital for every patient.
For more queries on the subject or consultations, visit https://drarvindkumar.com/contact-us.php.
FAQs
Why do lung transplant patients not live long?
Lung transplant patients comparably have a shorter life expectancy compared to patients who undergo other types of organ donation. It could be due to the side effects of prolonged immunosuppression or due to the eventual deterioration of the transplant lungs.
Are you on a ventilator after a lung transplant?
Yes, it is mandatory for patients to be on a ventilator after a lung transplantation surgery, at least until the transplanted lungs are strong enough to let the patient breathe on their own.
What is the biggest problem with lung transplants?
The biggest issue or complication with lung transplantation is a chronic rejection of the lung tissues of the transplanted lungs. This is primarily because the immune response of the lungs is a lot more compared to the other organs.

.webp)