

MBBS (AIIMS), MS (Surgery, AIIMS), MNAMS, FACS (USA), FICS (USA), FUICC
Tue, 23 Jan 2024
Hydatid cysts are parasite illnesses brought on by the larvae of a tapeworm called Echinococcus, often called echinococcosis or hydatid disease. The liver and lungs are the most prevalent organs in which these cysts appear in humans. Hydatid cysts are a serious health risk, particularly in areas where people and animals cohabit. For prevention and prompt management, it is critical to comprehend the transmission and etiology of hydatid cysts. To know more about it consult Dr. Arvind Kumar.
Dr Arvind Kumar is one of the best and renowned names in Chest and Robotic surgery in India. To get the best treatment consult us.
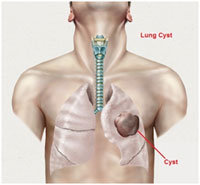
Cyst (hydatid cysts) in the lung is also referred to as echinococcosis or echinococcal disease. It results from an infection due to a tapeworm of genus Echinococcus. The disease may produce cysts in the liver, lungs, brain and other organs. It is seen in both men and women.
The life cycle of the Echinococcus tapeworm, which mostly affects canines (such as dogs) and herbivores, results in hydatid cysts. The adult tapeworm lives in the canine intestines and lays eggs there. The eggs are then released into the dogs feces, posing a risk of environmental contamination.
When people consume tainted food or drink, they unintentionally become hosts. The eggs hatch once they are inside the body of a person, and the larvae go to different organs where they develop into cysts. Due to their roles as filters, the liver and lungs are especially vulnerable.
In order to adopt preventative measures and make an early diagnosis of hydatid cysts, it is crucial to understand their intricate life cycle and mechanisms of transmission. If left untreated, such cysts can result in major health consequences.
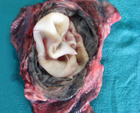
The hydatid cyst of the lung causes cough, chest pain and hemoptysis (coughing up blood).
Given the size, location, and length of growth, hydatid cyst symptoms might change. When the cysts reside within the liver, common symptoms include discomfort, swelling, and abdominal pain.
Chest discomfort, loss of breath, and coughing are all symptoms of lung cysts. In more extreme situations, the cysts may burst, leading to severe allergic responses and potentially fatal consequences.
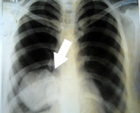
In order to see the cyst size or position, imaging tests like ultrasounds, CT scans, or MRIs are frequently used in diagnosis. Confirmation can be aided by blood tests that can identify particular antibodies linked to Echinococcus infection.
Diagnosis for hydatid cyst of lung is confirmed by X-rays, CT Scan and serological tests.
Lung hydatid cyst development can significantly affect respiratory health. Long-lasting coughing, chest discomfort, and difficulty breathing are among the symptoms brought on by these cysts as they expand and take up spaces within the lung tissue. Additionally, patients may cough up blood or phlegm that is rust-colored.
Hydatid cysts within the lungs can result in a number of consequences if left untreated. Cyst rupture, the most serious of them, can result in anaphylactic shock, a possibly fatal allergic response. Rupture can happen naturally or as a result of trauma, such as a fall or an accident.
Large cysts may also impose pressure on nearby lung tissue, which can cause atelectasis (lung collapse). Additionally, secondary bacterial infections might appear and exacerbate respiratory symptoms.
To avoid these consequences, it is essential to diagnose them quickly and take action. The most efficient technique to manage the impact on the lungs or stop additional harm is often by surgical excision of the cysts.
The main treatment objective for hydatid cysts is to get rid of them and stop them from coming again. The most effective method for removing hydatid cysts in the lungs is surgery. The method seeks to remove the cyst with the least amount of leakage or rupture danger, both of which can result in serious consequences.
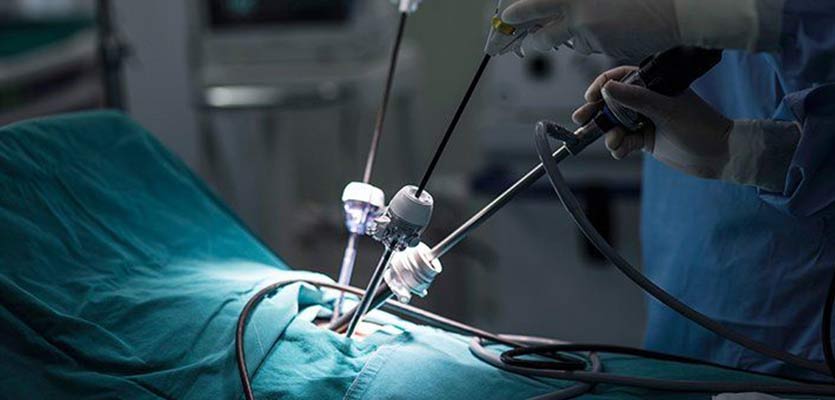
The cyst is cautiously separated from the bronchial tissue during surgery and removed. Surgeons may employ specialized methods like the "bagging" procedure, in which the cyst is contained in a sterilized bag before removal, to avoid the spread of the cysts contents. This confinement reduces the possibility of infections or allergic responses brought on by spills.
The tissue in the lungs is carefully checked after the cyst has been removed for any cyst remnants, which are then painstakingly removed. After that, the surgical area is sanitized and disinfected.
Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS), in particular for smaller cysts, may be appropriate in some circumstances. To remove the cyst using VATS, small incisions are made, and a tiny camera is used, along with specialized tools. This strategy often results in quicker postoperative pain relief and faster recovery timeframes.
Patients may require antiparasitic drugs after surgery to guarantee that any leftover parasite components are eliminated. Depending on the patients health and reaction to treatment, the duration of the drug may change.
An expert and qualified surgical team is necessary for the surgical removal of hydatid cysts, and meticulous postoperative surveillance is necessary to evaluate healing progress and identify any possible problems early. The best opportunity for total cyst removal and sustained healing is through surgery.
Copyright @ (Prof.) Dr. Arvind Kumar. All Rights Reserved / Thoracic Surgical Oncologis
License Number: U.P State Medical Council (India) No. 27637
