

MBBS (AIIMS), MS (Surgery, AIIMS), MNAMS, FACS (USA), FICS (USA), FUICC
Tue, 23 Jan 2024
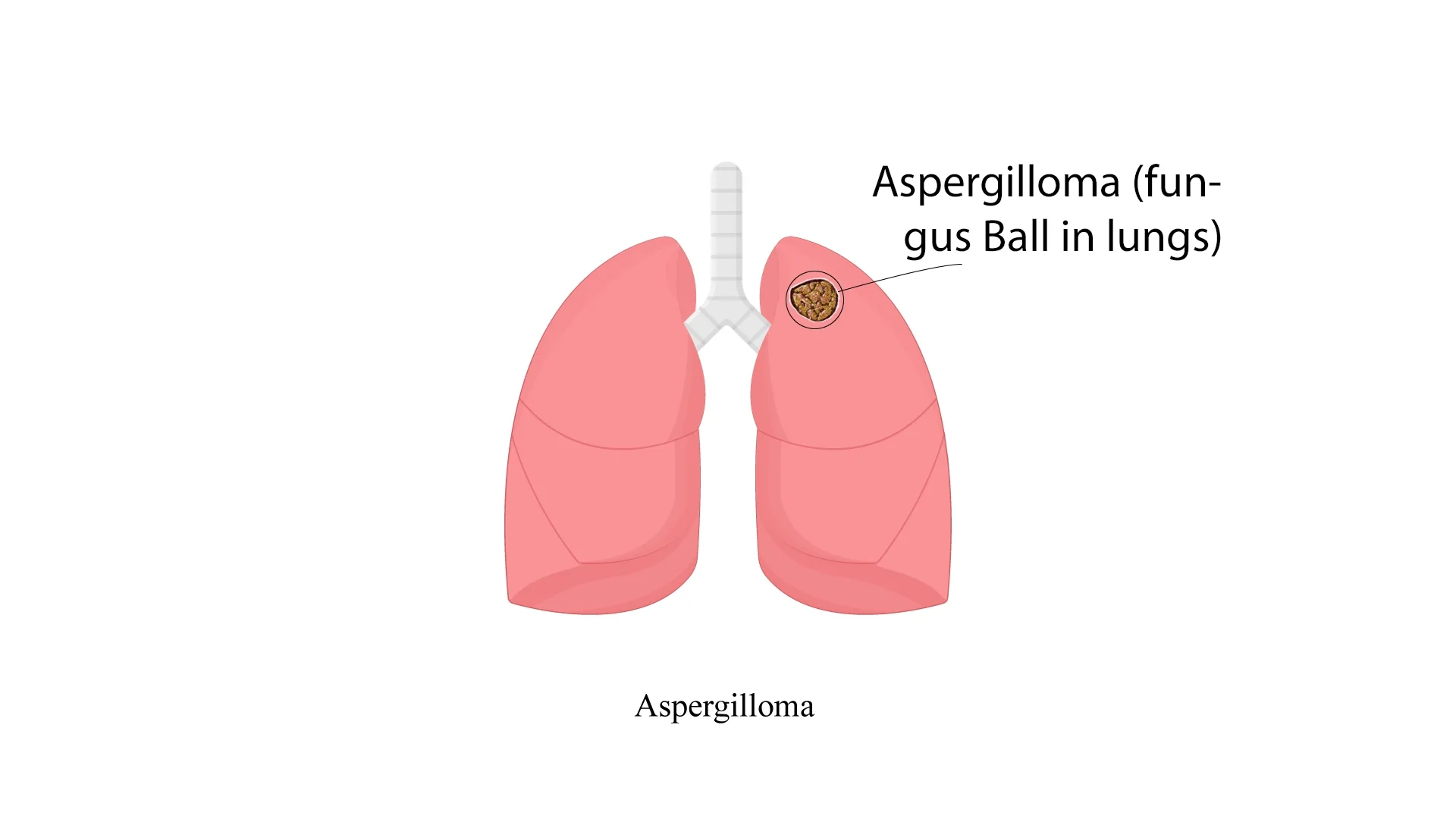
Aspergilloma, also known as mycetoma or fungus ball, is a fungal illness predominantly brought on by Aspergillus species. It frequently affects people who have certain underlying pulmonary disorders, which presents special diagnostic and treatment challenges. We dig into the complexities of aspergilloma in this thorough investigation, covering its reasons, symptoms, diagnosis, therapy, and prevention.
Aspergilloma is a very rare, exciting, and yet difficult disorder that may result from a fungal infection. It may lead to serious illness if left untreated. Consult one of the best chest surgeons, Dr Arvind Kumar, to get the expert treatment.
Aspergillus species, including Aspergillus fumigatus, are the ones responsible for aspergilloma, as the term implies. The development of a fungal ball, often referred to as a mycetoma, inside pre-existing lung cavities is what distinguishes this illness. These cavities are frequently the outcome of previous lung conditions like bronchiectasis or TB.
An Aspergilloma or Mucormycosis, also known as fungus ball, is a clump of fungus which can develop in a cavity in the lung.
Aspergillus spores, which are all around us, are what cause aspergilloma to develop. These spores are easily breathed in and are frequently found in dirt, dust, and decomposing debris. However, not every person who breathes in these spores will develop the symptoms and get an aspergilloma.
The inhaled spores have an excellent habitat to thrive in people who have predisposed characteristics, including pre-existing lung spaces or lung disorders like TB. Aspergillomas can arise when the fungus grows in these cavities and forms a thick fungal ball in a safe environment.
Aspergilloma patients may have a variety of symptoms.
These may consist of:
Fungal Ball in the lung occurs often after Tuberculous infection of the lung. Patients suffering from Aspergilloma or Mucormycosis generally complain of regular cough and at times, blood in the sputum. Sometimes, the blood in the sputum may be massive in amount. If you and any of your loved ones are suffering this issue then immediately consult the reliable surgeon.
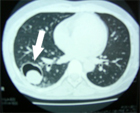
Making an aspergilloma diagnosis might be difficult. A clinical examination, imaging investigations, and laboratory testing are frequently combined in this process. Distinctive fungal balls within the lung cavities can be seen by radiographic imaging techniques including X-rays and CT scans. For confirmation of the existence of Aspergillus in respiratory secretions, a sputum culture may be carried out.
The diagnosis of Mucormycosis is suspected on the basis of clinical history and confirmed by CT scan. Although, many a times patients are prescribed anti-fungal medication, the only cure for Mucormycosis is complete removal of diseased part of the lung.
Aspergilloma treatment involves a diverse strategy. The intensity of the patients symptoms and general health will influence the therapy option.
Options for treatment include:
Treating Underlying Lung Conditions: In order to stop a return of aspergilloma, it is essential to treat and manage underlying lung conditions such bronchiectasis and TB.
Antifungal Drugs: In order to treat the infection, antifungal medications may be recommended. These drugs might not totally get rid of the fungus, though.
Embolisation. This technique prevents aspergilloma-related lung hemorrhage. Through a catheter that has been inserted into an artery supplying a lung cavity where the aspergilloma is triggering blood loss, a radiologist administers a substance to stop the blood loss. The injected substance hardens, blocks the areas blood supply, and stops the bleeding. The bleeding will likely resume after the procedure, which only briefly stops it.
Surgery: The afflicted lung cavity may need to be surgically removed in extreme situations when an aspergilloma produces substantial bleeding or is resistant to antifungal medication. Thoracotomy is the name of this technique.
Thoracotomy is crucial in instances of aspergilloma. The damaged lung tissue can be directly accessed during this surgery. The fungus ball can be accurately removed by surgeons, and they can also treat problems or fix lung damage. Thoracotomy is an important technique for successfully treating aspergilloma, restoring the function of the lungs, and improving the persons quality of life since it offers an unobstructed view and skillful movement.
Avoiding Aspergillus spore exposure and treating underlying pulmonary problems are the main components of aspergilloma prevention.
The following are some essential precautions:
In a world full of fungal diseases, Aspergilloma presents a unique set of difficulties due to its unusual fungal ball development. To avoid serious consequences, prompt diagnosis and care are crucial. For those who are in danger, it is essential to comprehend the risks and actively take preventive actions.
Copyright @ (Prof.) Dr. Arvind Kumar. All Rights Reserved / Thoracic Surgical Oncologis
License Number: U.P State Medical Council (India) No. 27637
